Introduction
Age-sex pyramids are fundamental tools in epidemiological analysis,
providing a visual representation of the demographic distribution of
cases. They help identify vulnerable populations, understand
transmission patterns, and guide public health interventions. The
age_sex_pyramid() function supports both line-list data
(individual cases) and pre-aggregated counts so that analysts can tailor
output to their workflows.
Example 1: Static pyramid from line-list data
Static pyramids are ideal for publications and reports where a clear,
printable summary of the population structure is required. In this
example we subset epiviz::lab_data to Staphylococcus aureus
detections recorded during 2023 and let age_sex_pyramid()
calculate the age bands automatically from the line-list data.
Prepare the line-list data
line_list_pyramid_data <- epiviz::lab_data %>%
filter(
organism_species_name == "STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS",
specimen_date >= as.Date("2023-01-01"),
specimen_date <= as.Date("2023-12-31"),
!is.na(date_of_birth),
!is.na(sex)
) %>%
mutate(
sex_clean = case_when(
toupper(sex) %in% c("M", "MALE") ~ "Male",
toupper(sex) %in% c("F", "FEMALE") ~ "Female",
TRUE ~ NA_character_
)
) %>%
filter(!is.na(sex_clean))Plot the static pyramid
age_sex_pyramid(
dynamic = FALSE,
params = list(
df = line_list_pyramid_data,
var_map = list(
dob_var = "date_of_birth",
sex_var = "sex_clean"
),
grouped = FALSE,
mf_colours = c("#440154", "#2196F3"),
x_breaks = 6,
x_axis_title = "Number of detections",
y_axis_title = "Age group (years)",
chart_title = "Static age-sex pyramid",
age_calc_refdate = as.Date("2023-12-31")
)
)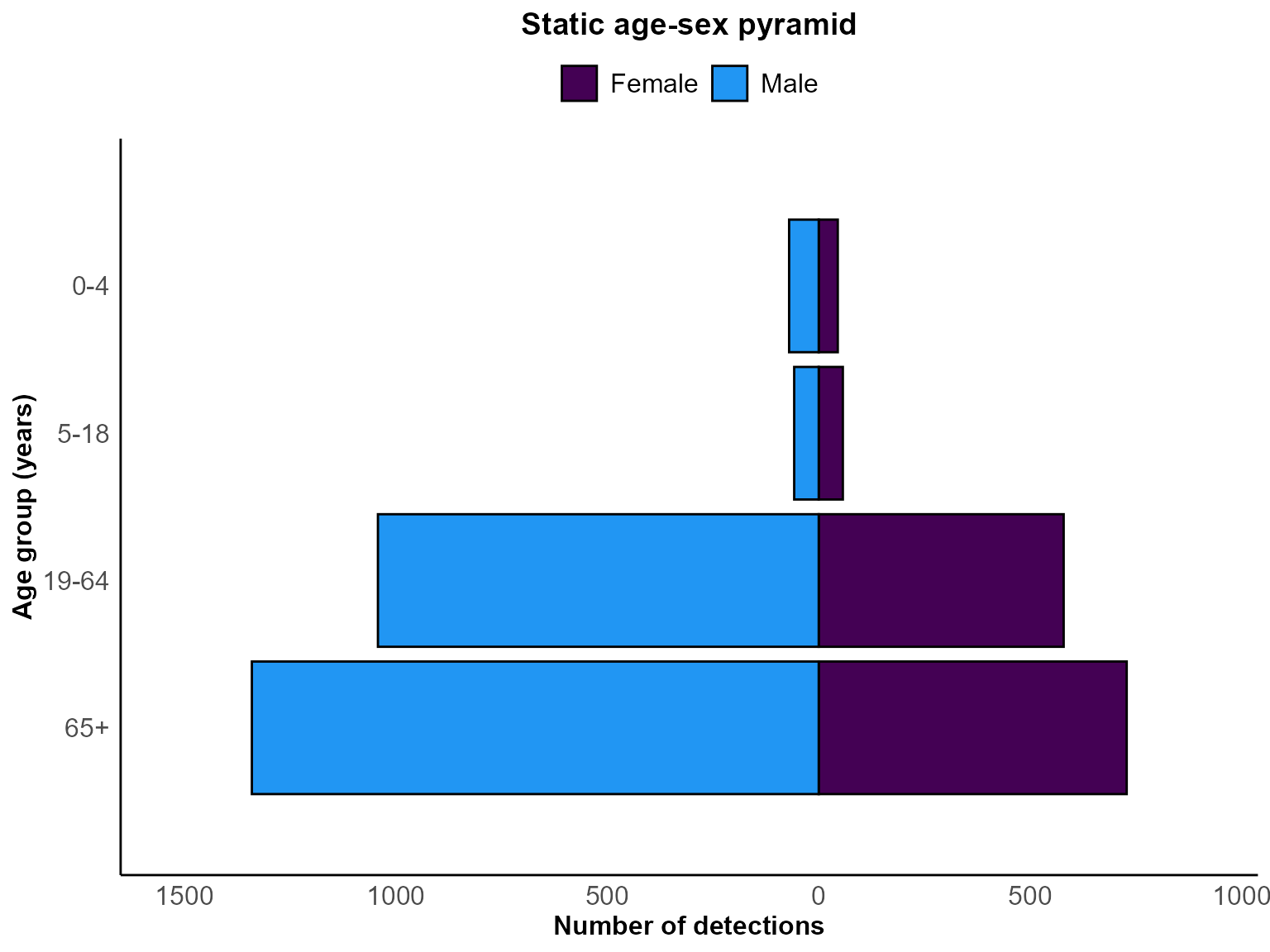
Age-sex pyramid for Staphylococcus aureus detections between January and December 2023.
Interpretation: The plot highlights the age groups contributing most to laboratory detections, with mirrored bars showing the relative burden among males and females.
Example 2: Interactive grouped pyramid with confidence intervals
Interactive pyramids are useful for exploratory dashboards where end users can interrogate the data directly. By aggregating the same records into age bands and providing the associated Poisson confidence intervals, the plot reveals both the central estimates and their uncertainty.
Aggregate counts and calculate confidence intervals
grouped_pyramid_data <- line_list_pyramid_data %>%
mutate(
age_years = floor(time_length(interval(date_of_birth, as.Date("2023-12-31")), "years")),
age_band = cut(
age_years,
breaks = c(0, 5, 15, 25, 35, 45, 55, 65, 75, 85, Inf),
right = FALSE,
labels = c("0-4", "5-14", "15-24", "25-34", "35-44",
"45-54", "55-64", "65-74", "75-84", "85+")
)
) %>%
filter(!is.na(age_band)) %>%
count(age_band, sex_clean, name = "val") %>%
rename(sex_mf = sex_clean) %>%
mutate(
lower_ci = if_else(val == 0, 0, qchisq(0.025, 2 * val) / 2),
upper_ci = qchisq(0.975, 2 * (val + 1)) / 2
)Plot the interactive grouped pyramid
age_sex_pyramid(
dynamic = TRUE,
params = list(
df = grouped_pyramid_data,
var_map = list(
age_group_var = "age_band",
sex_var = "sex_mf",
value_var = "val",
ci_lower = "lower_ci",
ci_upper = "upper_ci"
),
grouped = TRUE,
ci = "errorbar",
mf_colours = c("pink", "blue"),
x_breaks = 5,
chart_title = "Interactive grouped pyramid with CI",
x_axis_title = "Number of detections",
y_axis_title = "Age group (years)",
legend_title = "Sex"
)
)Interactive age-sex pyramid with 95% confidence intervals for Staphylococcus aureus detections in 2023.
Interpretation: The interactive plot provides hover labels for precise counts and asymmetric confidence intervals, enabling rapid assessment of uncertainty for each age-sex combination.
Tips for age-sex pyramids
-
Data preparation: For line-list data
(
grouped = FALSE), ensure your date-of-birth and sex variables are present and clean; the function can derive age groups from dates directly. -
Variable mapping: Use
var_mapto align your column names with the expected inputs. Grouped data requiresage_group_var,sex_var,value_var,ci_lower, andci_upper. -
Confidence intervals: Set
ci = "errorbar"with grouped data after supplying interval bounds, or allow the function to calculate Poisson intervals when working with line lists. -
Colour choices: Provide
mf_coloursto match organisational palettes or accessibility requirements (e.g., colour-blind friendly combinations). -
Reference dates: Control age calculation with
age_calc_refdateto ensure comparisons are aligned to a consistent snapshot in time, especially for retrospective analyses.
